Elestic Deformation Of Ceramics

Pask materials and molecular research division lawrence berkeley laboratory and department of materials science and engineering university of california berkeley calif.
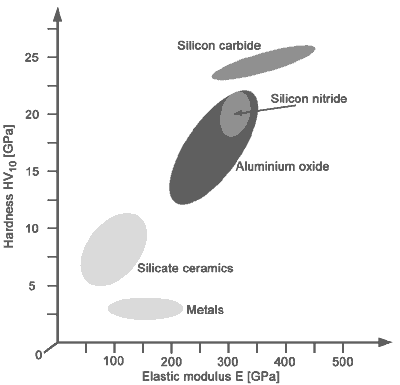
Elestic deformation of ceramics. Understanding elastic deformation is very important in ceramics to eliminate instantaneous brittle fracture at some applied stress levels. A temporary shape change that is self reversing after the force is removed so that the object returns to its original shape is called elastic deformation. Elastic deformation of metals and ceramics is commonly seen at low strains. It is due to several unique properties such as relatively low mass low fractional density low thermal conductivity resistance to chemical attack high specific surface area high permeability and resistance to high temperature and thermal cycling.
Above that the material breaks without neck formation this is elastic deformation. Particle size determines the physical properties. When the applied loads are removed metals return to their original shape. Ceramics are generally brittle or ductile in nature.
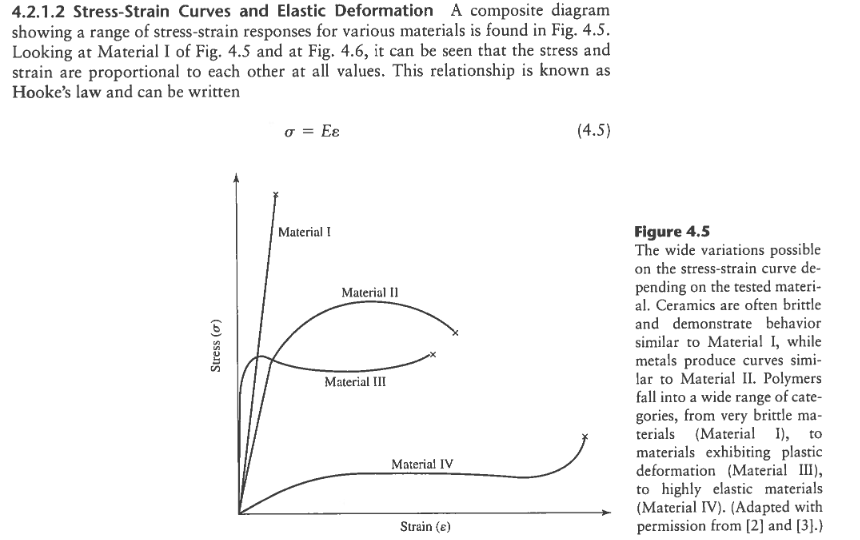
Understanding elastic deformation is very important in ceramics to eliminate instantaneous brittle fracture at some applied stress levels. When a sufficient load is applied to a metal or other structural material it will cause the material to change shape. Their elastic behavior is generally linear. This temporary deformation of metals is.
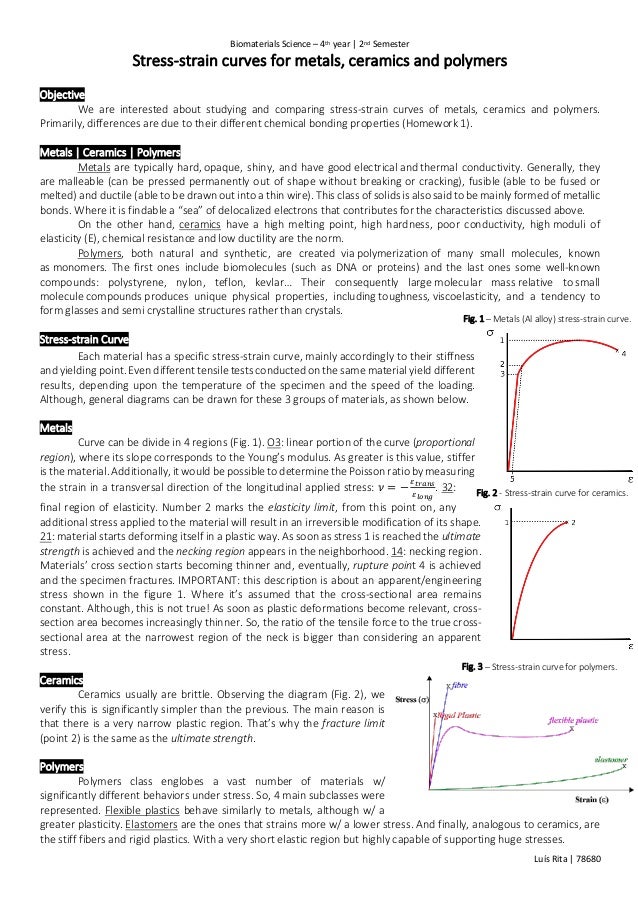
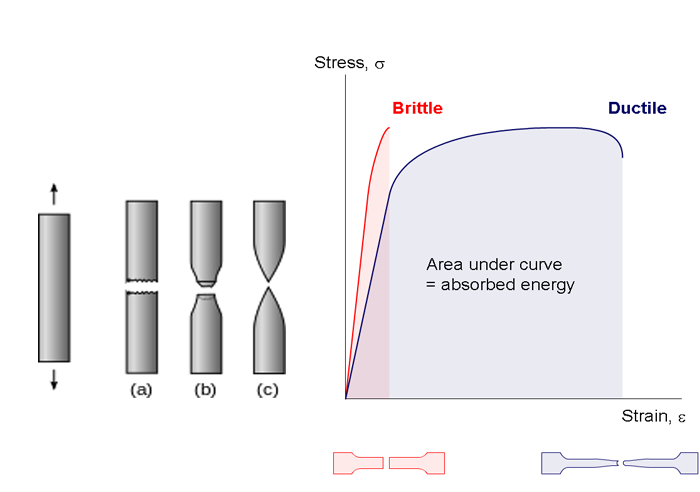
It is difficult to measure the yield strength of ceramics as they tend to fracture before they enter the plastic deformation region i e they are brittle. Elastic deformation refers to a certain amount of deformation of the material under the action of external force. Materials science and engineering 25 1976 77 86 77 elsevier sequoia s a lausanne printed in the netherlands plastic deformation of ceramic materials philip c. If we apply the load the material will deform up to the material can withstand the load.
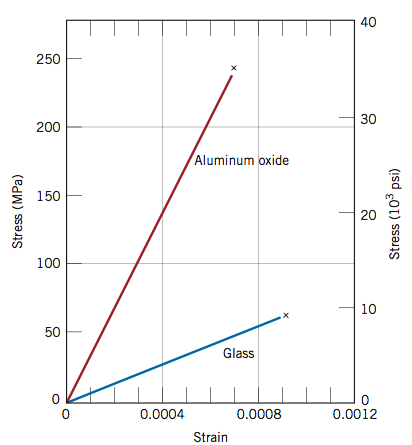
Dokko and joseph a. Porous ceramics are a class of materials used in several applications of industrial and engineering branch. As the curve transitions from the elastic to plastic deformation typically there is a peak stress. Examples of two brittle materials that fracture before entering the plastic deformation region are aluminum oxide and glass as shown in the figure below.
1 metal materials generally undergo two stages of. A highly elastic polymer may stretch over 10 times the original length before breaking. The fracture stress is usually the same or very close to the elastic limit. This change in shape is called deformation.
Its behavior begins in the linear elastic deformation region. Deformation can be elastic or plastic. Likewise here stress and strain determine the strength of the material. When metals are placed under small loads or stresses they deform.
For polymer materials this peak stress is identified as the yield stress. After the external force is removed the material can return to the original shape of deformation. So what are the characteristics of elastic deformation of zirconia ceramics.